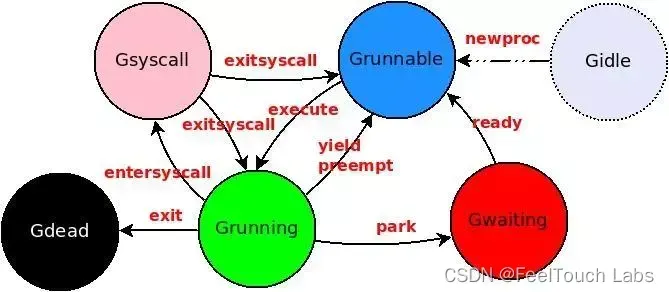
// Create a new g in state _Grunnable (or _Gwaiting if parked is true), starting at fn.
// callerpc is the address of the go statement that created this. The caller is responsible
// for adding the new g to the scheduler. If parked is true, waitreason must be non-zero.
func newproc1(fn *funcval, callergp *g, callerpc uintptr, parked bool, waitreason waitReason) *g {
if fn == nil {
fatal("go of nil func value")
}
mp := acquirem() // disable preemption because we hold M and P in local vars.
pp := mp.p.ptr()
// 尝试复用dead状态协程,从空闲列表中获取
newg := gfget(pp)
if newg == nil {
// 如果没有可以复用的,申请一个新的协程,并从堆中申请一块内存,初始化他的栈
newg = malg(stackMin)
// 暂时设置成消亡态去禁止gc扫描
casgstatus(newg, _Gidle, _Gdead)
allgadd(newg) // publishes with a g->status of Gdead so GC scanner doesn't look at uninitialized stack.
}
if newg.stack.hi == 0 {
throw("newproc1: newg missing stack")
}
if readgstatus(newg) != _Gdead {
throw("newproc1: new g is not Gdead")
}
totalSize := uintptr(4*goarch.PtrSize + sys.MinFrameSize) // extra space in case of reads slightly beyond frame
// 栈对齐
totalSize = alignUp(totalSize, sys.StackAlign)
sp := newg.stack.hi - totalSize
if usesLR {
// caller's LR
*(*uintptr)(unsafe.Pointer(sp)) = 0
prepGoExitFrame(sp)
}
// 清除内存
memclrNoHeapPointers(unsafe.Pointer(&newg.sched), unsafe.Sizeof(newg.sched))
// 设置调度相关字段
newg.sched.sp = sp
newg.stktopsp = sp
// 确保协程执行结束后,跳转到goexit
newg.sched.pc = abi.FuncPCABI0(goexit) + sys.PCQuantum // +PCQuantum so that previous instruction is in same function
newg.sched.g = guintptr(unsafe.Pointer(newg))
gostartcallfn(&newg.sched, fn)
newg.parentGoid = callergp.goid
newg.gopc = callerpc
newg.ancestors = saveAncestors(callergp)
// 设置入口函数
newg.startpc = fn.fn
// 如果是系统Goroutine
if isSystemGoroutine(newg, false) {
sched.ngsys.Add(1)
} else {
// 对用户栈执行profile相关处理
if mp.curg != nil {
newg.labels = mp.curg.labels
}
if goroutineProfile.active {
// A concurrent goroutine profile is running. It should include
// exactly the set of goroutines that were alive when the goroutine
// profiler first stopped the world. That does not include newg, so
// mark it as not needing a profile before transitioning it from
// _Gdead.
newg.goroutineProfiled.Store(goroutineProfileSatisfied)
}
}
// 将一个栈添加到垃圾回收器的扫描任务中
gcController.addScannableStack(pp, int64(newg.stack.hi-newg.stack.lo))
// 修改协程状态为运行态
var status uint32 = _Grunnable
casgstatus(newg, _Gdead, status)
if pp.goidcache == pp.goidcacheend {
// Sched.goidgen is the last allocated id,
// this batch must be [sched.goidgen+1, sched.goidgen+GoidCacheBatch].
// At startup sched.goidgen=0, so main goroutine receives goid=1.
pp.goidcache = sched.goidgen.Add(_GoidCacheBatch)
pp.goidcache -= _GoidCacheBatch - 1
pp.goidcacheend = pp.goidcache + _GoidCacheBatch
}
newg.goid = pp.goidcache
pp.goidcache++
newg.trace.reset()
...
releasem(mp)
return newg
}
|